Next: References, Previous: Continuous Deployment (CD), Up: Pronghorn [Contents]
7 Discussion and Conclusions
Legacy workflows, characterized by manual and disjointed processes, have proven to be inefficient and error-prone. They often lack automation, version control, and collaboration mechanisms, leading to delays, inconsistencies, and difficulties in managing software projects. Recognizing these challenges, the project sought to revolutionize the software development lifecycle by adopting modern practices and tools.
By embracing CI/CD and GitOps, developers can automate the build, testing, and deployment processes, leading to faster and more reliable software delivery. GitFlow and TBD provided contrasting strategies for managing code branches and version control, with GitFlow emphasizing branch-based isolation and TBD favoring a simpler, trunk-based approach. Both models offered benefits in terms of collaboration, code management, and release cycles. All these workflows are possible thanks to different technologies, such as containerization or container orchestration, which allow the creation of lightweight and portable application environments, and their consistency, scalability, and efficiency across different deployment targets. Moreover, declaring all the underlying infrastructure as IaC simplifies infrastructure provisioning, configuration, and management, and makes it easier to reproduce environments and maintain consistency across deployments.
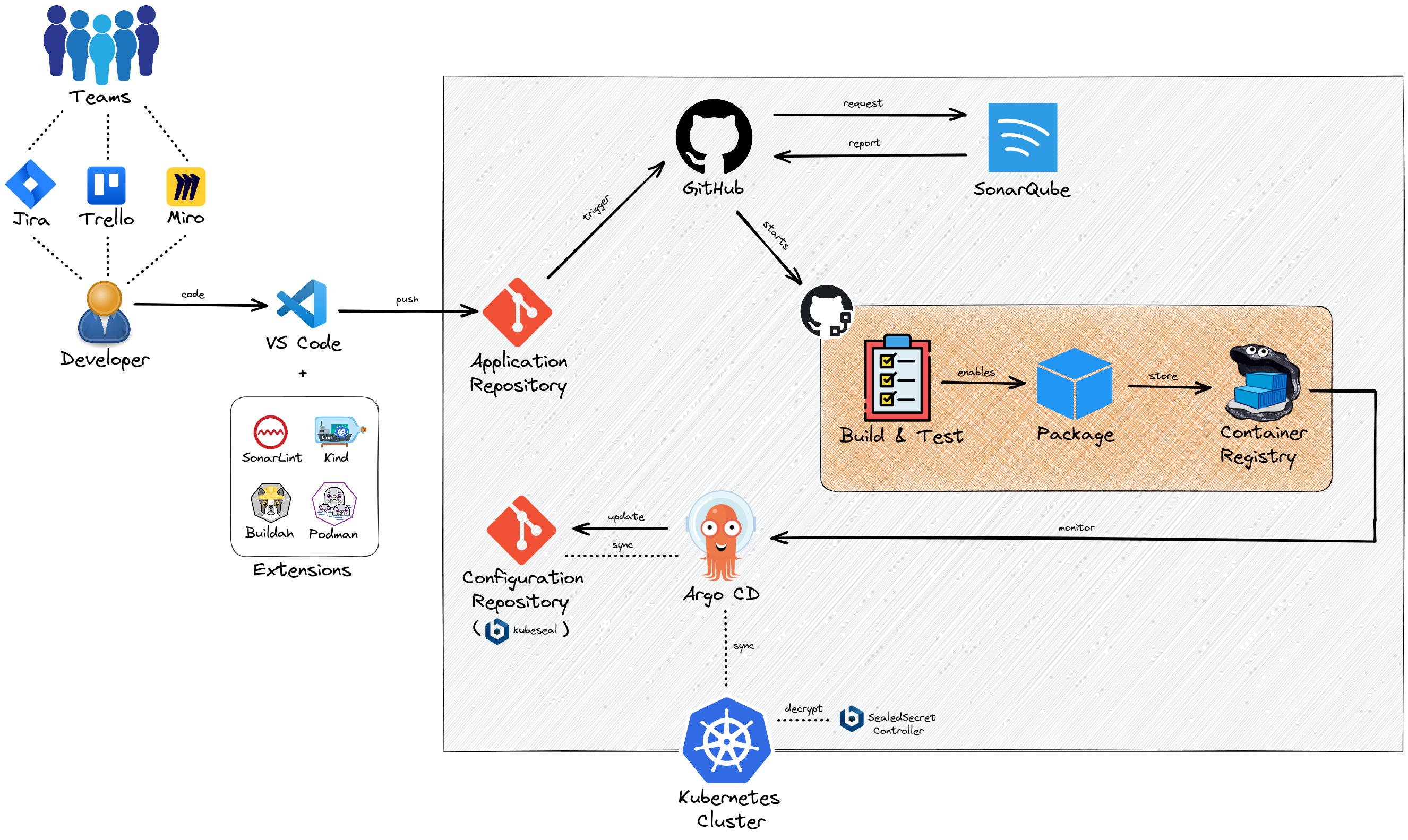
Figure 7.1: Full Pronghorn CI pipeline and GitOps diagram
Overall, this transformation project from legacy workflows to modern software development and deployment practices, makes possible for individuals, groups of enthusiasts, and organizations can make applications and programs which achieve an improved efficiency, collaboration, and reliability, enhancing also code quality, and enables faster and more secure deployments.